Closing the MSME funding gap: How digital lenders can help increase financial inclusion
SMEs have been an important contributor to the global economy for a long time. However, in the current financial environment, they are facing funding hurdles more than ever, leading to a MSME funding gap of $5.2 Billion. Digital lending has the potential to offer much-needed support while offering a strong opportunity for professional and institutional investors if approached correctly.
MSME
Micro, small and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) are an important part of the global economy, as their contribution to job creation plays an important role in economic growth, particularly in emerging economies. According to The World Bank: “They represent about 90% of businesses and more than 50% of employment worldwide. Formal SMEs contribute up to 40% of national income (GDP) in emerging economies” [1] Nevertheless, there are many constraints to the growth of MSMEs, one of which is a lack of funding.
MSME are less likely to obtain bank loans than large firms as traditionally a part of this sector is not able to provide the required collateral for conventional collateral-based bank lending, nor are their returns or growth prospects high enough to attract formal venture capitalists and other risk-loving investors. These factors have led to a notable funding gap for these kinds of businesses. A direct result of this funding gap is that MSMEs have to rely on alternative ways of funding such as internal funds and cash from family and friends.
With the ongoing Covid-19 pandemic the MSME have been affected in multiple ways. On the one hand, the labor supply is decreasing because many workers are sick or have to take care of family members. On the other hand, demand witnessed a strong decrease, which in certain sectors still has not entirely subsided, which leads to certain MSMEs not being fully functional and having to overcome liquidity bottlenecks.[2]
This leaves these businesses with no other option than borrowing a loan to overcome the pandemic shortage, which can prove to be troublesome when they are not able to provide banks with the required collateral. Furthermore, due to current regulations, small loans in this area are not attractive for banks in their current non-digital setup as they only see marginal profits at best. So how can digital lenders help extend access to financial products and services to MSME in need of funding and therefore reduce the funding gap? The digital nature of these offers holds the solution to many of the inherent problems faced by MSME and could prove to be a serious accelerator to the economy while serving a more profound egalitarian purpose.
The World Bank reports that various influences such as poverty, distance to financial institutes, education, gender, income, and age lead to about 1.7 billion adults still being unbanked as of 2017. [3] This means that many people in the world still do not have affordable and useful access to financial products and services. As a result, these people are not able to operate in the financial sector. This is one of the reasons why the MSME funding gap has emerged. In short, an increase in financial inclusion is of great importance to narrow the MSME funding gap. According to a new publication, which the Atlantic Council has published, “Financial inclusion is central to promoting inclusive growth and shared prosperity.” [4] In summary, it can be concluded that the advancement of financial inclusion has to be considered a key factor in reducing the MSME funding gap.
Impact of digitalization on digital lending
As a result of smartphone usage and internet diffusion, which rose sharply during the Covid-19 pandemic, digital lenders were able to simplify financial inclusion for the unbanked population, enabling them to apply for loans from the comfort of their homes with a quicker process, be it in the country’s hinterlands or in the big city. Any provider that wants to keep up in today's fast-growing digital world must be able to constantly adapt to new developments in order to secure their position in certain segments. One of these segments is the MSME segment, which continues to gain importance.
This leads to accelerated growth in product providers, therefore increasing competition. This development is a serious threat to the banks, as many MSMEs often prefer loans from alternative providers, as they can bypass the non-transparent, time-consuming, and bureaucratically overloaded processes of the banks and also receive individual offers. [5] By means of financial inclusion, digital lending hence offers a valid opportunity for effectively reducing the MSME funding gap.
THE MSME funding gap
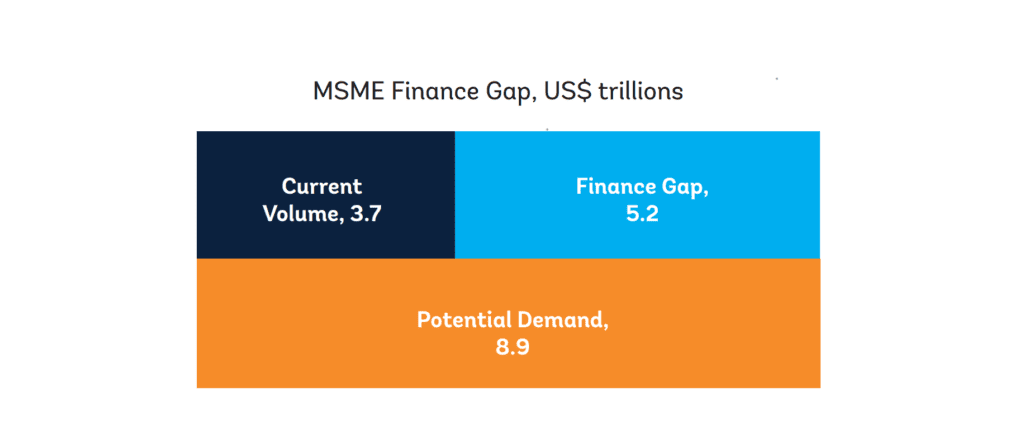
The MSME funding gap has been an obstacle to economic growth in developing economies for some time. As reported by IFC there is a total of $8.9 trillion in potential demand for MSME finance, of which only $3.7 trillion is served today. Meaning there is a $5.2 trillion funding gap.[6]
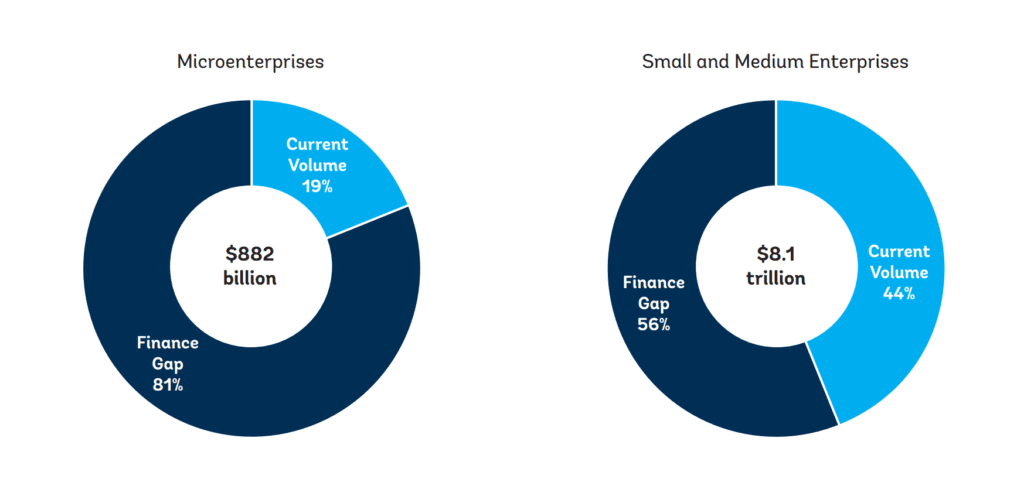
Proportionately to the entire needed financing sum, microenterprises face a much larger funding gap, as only 19% of the current volume is funded whereas SME see at least 44% funded. However, when comparing these gaps in absolute terms SME by far make up the largest part of the total MSME funding gap, with a whopping 86% of the sum. [7]
In many developing economies, some MSMEs do not even have access to the most basic business banking services. According to “The 2nd Global Alternative Finance Market Benchmarking Report by the University of Cambridge, in 2021” 4% of customers in the P2P/ Marketplace Business Lending were categorised as unbanked and 30% as underbanked.[8]
Digital lending as problem solver
According to a study by the McKinsey Institute, all financial services combined could reduce costs by 80-90% by digitizing and digitalising their services. [9] One of the key aspects of narrowing the MSME funding gap is a reduction of costs involved in lending.This is where digital lending can shine. The sleek and efficient functionality of digital lending allows for considerable cost-saving opportunities when compared with traditional non-digital bank lending.
Digital lending is not only lowering the cost of providing financial services but also helps to find a way around MSMEs’ insufficient credit history or lack of securitised assets and collateral by being able to collect and analyse data digitally. Many lenders use smart algorithms to determine the risk associated with a loan, allowing them to offer loans where sufficient collateral or other securities would not be available. Using this leverage can be a substantial contributor to the narrowing of the MSME funding gap, with more and more MSMEs being able to overcome their financial constraints.
The MSMEs insufficient financial inclusion and the resulting funding gap are not entirely new problems, however, the issue has been exacerbated by the Covid-19 pandemic. Alternative financing such as digital lending may be an active solution in the battle for financial inclusion since fintech companies are already well positioned to issue loans to MSMEs who have a hard time getting a loan from the bank.
The good news is that this increase in service quality and availability does not stem from a purely altruistic background, but rather is to be seen as a natural evolution of the market. FinTechs are helping in making the financial sector more performance-driven and efficient, hence offering chances all along the value chain. Cost savings are achieved but at the same time, interesting opportunities for profit are made available to savvy investors. This development, which is currently also gaining attention from professional and institutional investors, allows for investment opportunities that profit from all the digital lending advantages in the areas of cost and time efficiency.
Lastly, an influx of financing which leads to a reduction of the funding gap should lead to a general economic acceleration which will then again create new opportunities for both investors and business owners. Digital lending alone may not be able to solve all the problems leading to- and stemming from the financing gap for MSME, but it certainly can be a great contributor to a holistic solution.
So what does this mean for professional and institutional investors looking for investment opportunities in digital lending?
Particularly in the current negative interest environment investors are looking for an alternative, yield-bringing investment opportunities away from traditional bonds. Digital lending has all the characteristics needed to fill this gap. Nevertheless, the digital lending market is extremely fragmented which makes it difficult for investors to invest large sums of money efficiently while still maintaining a secure and diversified portfolio. Thanks to our proprietary software, we are able to open the doors to digital lending for professional and institutional investors.
Enabling them to generate a diversified portfolio, which allows them to harness the benefits of digital lending. We enable professional investors to generate stable returns thanks to multi-layer diversification, resulting in low volatility and low correlation to any other asset class. Digital lending can be an interesting and profitable venture if approached correctly and with the right partners. Get in touch with us, to learn how we can help you with the software-based management of any type of digital lending data, structuring solutions, and advisory services.
[1] World Bank SME Finance: Development news, research, data | World Bank
[2] Coronavirus (COVID-19): SME policy responses (oecd.org)
[3] 2017 Findex full report_chapter2.pdf (worldbank.org)
[4] Inclusive growth needs financial inclusion. Can Central Bank Digital Currency help? - Atlantic Council
[5] ME-Lending im Wandel: Chancen zur Entwicklung zukunftsorientierter Geschäftsmodelle | Roland Berger
[6] World Bank Document (ifc.org)
[7] World Bank Document (ifc.org)
[8] 2020-04-22-ccaf-global-alternative-finance-market-benchmarking-report.pdf (cam.ac.uk) and CCAF-Global-Benchmark-Report-2021-v0_6.pdf (crowdfundinsider.com)
[9] MGI-Digital-Finance-For-All-Executive-summary-September-2016.ashx (mckinsey.com)


